Decades of scientific evidence demonstrate unequivocally that human activities jeopardise life on Earth. Dangerous anthropogenic interference with the climate system compounds many other drivers of global change.
Governments concur: the science is settled. But governments have failed to act at the scale and pace required. What should climate change scientists do?
There is an unwritten social contract between science and society. Public investment in science is intended to improve understanding about our world and support beneficial societal outcomes. However, for climate change, the science-society contract is now broken.
The failure to act decisively is an indictment on governments and political leaders across the board, but climate change scientists cannot be absolved of responsibility.
As we write in an article about this conundrum, the tragedy is the compulsion to provide ever more evidence when the phenomena are well understood and the science widely accepted. The tragedy is being gaslighted into thinking the impasse is somehow our fault, and we need to do science differently: crafting new scientific institutions, strategies, collaborations and methodologies.
Yet, global carbon dioxide emissions are 60% higher today than they were in 1990, when the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) published its first assessment. At some point we need to recognise the problem is political and that further climate change science may even divert attention away from where the problem truly lies.
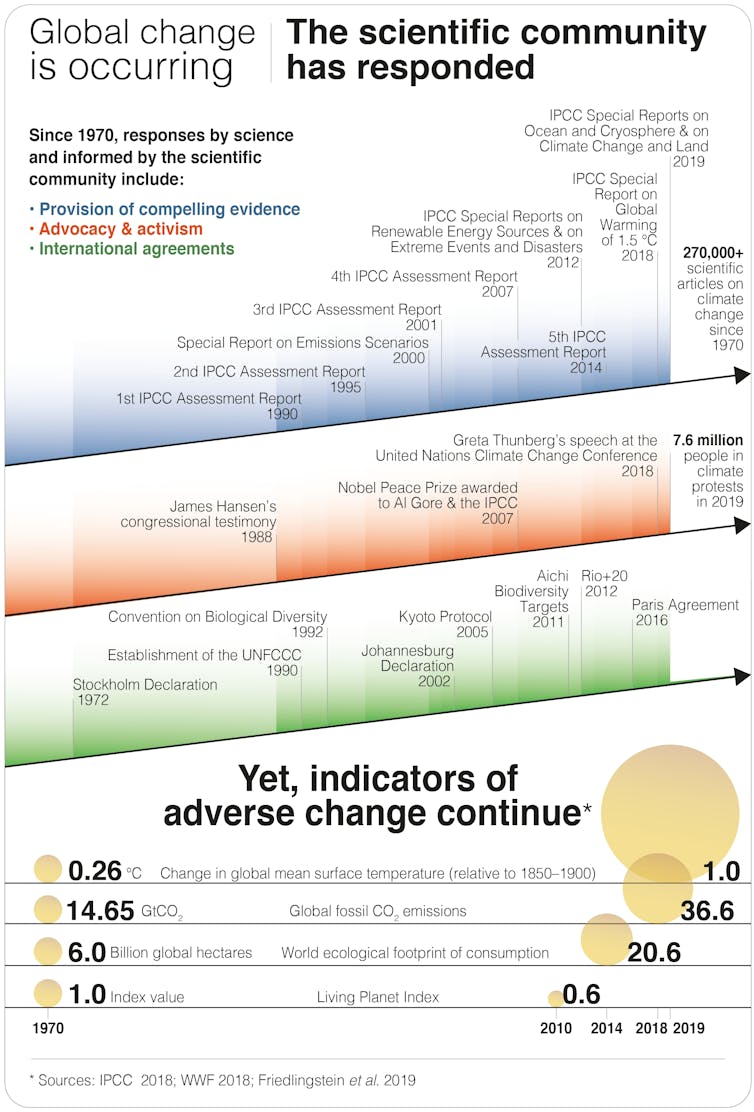
Governments agree that the science is settled but scientists are compelled to do more research despite inadequate government action and worsening climate change. Author provided, CC BY-ND
Was COP26 too little, too late?
The outcome of COP26, summarised in the draft Glasgow Climate Pact, includes some progress, including an agreement to begin reducing coal-fired power, removing subsidies on other fossil fuels, and a commitment to double adaptation finance to improve climate resilience for countries with the lowest incomes.
But many of the world’s leading scientists argue that this is too little, too late. They note the failure of COP26 to translate the 2015 Paris Agreement into practical reality to keep global warming below 1.5℃ above pre-industrial levels.
Even if COP26 commitments are fulfilled, there is a strong likelihood that humanity and life on Earth face a precarious future.
What are climate change scientists to do in the face of this evidence? We see three possible options — two that are untenable, one that is unpalatable.
Where to from here for climate change scientists?
The first option is to collect more evidence and hope for action. Continue the IPCC process that stays politically neutral and abstains from policy prescriptions. A recent editorial in Nature called on scientists to do just that: stay engaged to support future climate COPs.
However, this choice not only ignores the complex relationship between science and policy, it runs counter to the logic of our scientific training to reflect and act on the evidence. We know why global warming is happening and what to do. We have known for a long time.
Governments just haven’t taken the necessary action. In a recent Nature survey, six in ten of the IPCC scientists who responded expect 3℃ warming above pre-industrial levels by 2100. Persisting with this first option is therefore untenable.
The second option is more intensive social science research and climate change advocacy. As Harvard historian Naomi Oreskes recently observed, the work of the IPCC’s Working Group I (WGI, on the physical science basis of climate change) is complete and should be closed down. Attention needs to focus on translating this understanding into action, which is the realm of WGII (on impacts, adaptation and vulnerability) and WGIII (on mitigation of greenhouse gas emissions).
In parallel, growing numbers of scientists are getting involved in diverse forms of advocacy, including non-violent civil disobedience.
At #COP26, members of the activist group @ScientistRebel1 have chained themselves to a Glasgow bridge, sailed a dinghy down the River Clyde and glued themselves to a giant research paper outside the offices of a power company. (1/6) pic.twitter.com/jte58LRb5Q
— nature (@Nature) November 12, 2021
However, albeit more promising than option one, there is little evidence of impact thus far and it is doubtful this pathway will lead to the urgent transformative actions required. This option is also not tenable.
Halt on IPCC work until governments do their part
The third option is much more radical, but unpalatable. We call for a moratorium on climate change research that does little more than document global warming and maladaptation.
Attention needs to focus on exposing and re-negotiating the broken science-society contract. Given the rupture to the contract outlined here, we call for a halt on all further IPCC assessments until governments are willing to fulfil their responsibilities in good faith and mobilise action to secure a safe level of global warming. This option is the only way to overcome the tragedy of climate change science.
Readers might agree with our framing of this tragedy but disagree with our assessment of options. Some may want greater detail on what a moratorium could encompass or worry it may damage the credibility and objectivity of the scientific community.
However, we question whether it is our “duty” to use public funds to continue to refine the state of climate change knowledge (which is unlikely to lead to the actions required), or whether a more radical approach will serve society better.
We have reached a critical juncture for humanity and the planet. Given the unfolding tragedy, a moratorium on climate change research is the only responsible option for revealing and then restoring the broken science-society contract. The other two options are seductive but offer false hope.
We would like to acknowledge the work by Andrés Alegría in preparing the graphic.
Teaser Photo by Red Zeppelin on Unsplash





